When people think of artificial intelligence (AI), they usually think of planet-killing humanoids like Ultron or Isaac Asimov’s dystopia in I, Robot. Fortunately, modern-day AI is not remotely close to superseding human-level thinking capabilities. However, AI is growing and is already a part of our daily lives. From voice recognition software to song recommendations from Spotify, AI helps personalize people’s lives while making the world faster and safer. The healthcare industry, in particular, is working to utilize AI to assist medical professionals worldwide. So what is AI? And how is it being used in healthcare?
The definition of artificial intelligence includes the imitation of the human mind by machines and computers. AI is a vast field that includes computer vision (seen in self-driving cars) to natural language processing. The most popular type of AI is machine learning, which uses algorithms to learn from past data to make predictions about the future. AI continues to be a vital tool in the healthcare industry and biomedical research as researchers are able to collect various biological data from genomic sequences to evolutionary taxons. With the rise of data in biomedical research, AI has the potential to improve medical diagnosis, drug discovery, and healthcare interactions.
Medical Diagnosis
Diagnosing a medical condition or disease is one of the most important stages of combating a health threat. Human diagnosis involves matching symptoms to a particular disease through fluid samples or x-ray scans. AI can accelerate and cheapen the diagnosing process by efficiently corresponding certain patterns to specific conditions. AI researchers can create machine learning models to learn from health data and predict whether a new patient has or will contract a disease. In fact, many of these medical datasets are publicly available including breast cancer diagnoses collected by researchers from the University of Wisconsin. Data can range from demographics to health history such as smoking habits. In addition, almost every hospital uses Electronic Health Records (EHR) to virtually store important patient history. With permission from patients, hospitals can compile large datasets of EHR to provide AI developers with quality information to feed AI models.
More advanced AI can help with visuals and audio diagnosis. Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, involves the development of artificial neural networks that mimic the neurons in the human brain. Such neural networks can learn from images and even sounds to predict what category a specific image or sound belongs to. In the context of healthcare, medical professionals can use algorithms that analyze MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scans to predict if a patient has pneumonia or electrocardiograms to analyze abnormal heart beating. In addition, various image segmentation techniques can help improve the accuracy of neural networks by separating images into many regions and identifying contours and key features of a disease or condition.
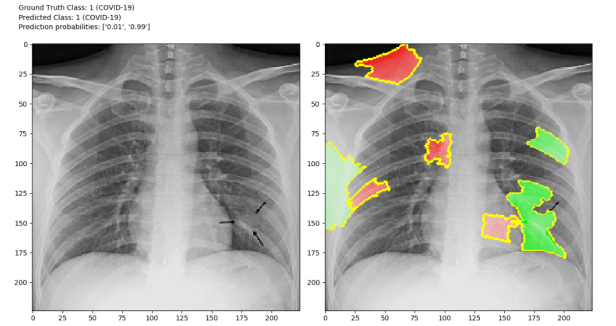
Image segmentation and deep learning analysis on x-ray images to diagnose pneumonia in COVID-19. Image from data scientist Blake VenBerlo.
Drug Discovery
Drug Discovery is the stage of identifying a potential medicine to push to the public market. The drug discovery process takes 3-5 years usually involving the identification of around 5,000 to 10,000 potential drugs. Even with thousands of potential drugs, usually, only one is officially sold on the market. Drug development is a lengthy, expensive, and tedious process but AI can assist pharmaceutical scientists to find viable drugs quicker and easier. Using past data on molecules and compounds that have shown to be biologically active or inactive, researchers can create models that take in a new drug design and predict its potential bioactive response which can eliminate ineffective drugs early on. Since a molecule’s structure is correlated to its function, researchers can specifically use AI to analyze the chemical composition of compounds including atomic bonding and ring structures to predict its inhibition or activation toward a gene or protein that plays a significant role in disease.
Health Care Assistance
AI can also be used to assist patients in their interactions with hospitals. Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a type of AI that analyzes human dialects. One example almost everyone has used is email filters that classify emails that are spam by identifying key phrases or words often associated with spam emails. Researchers can use NLP to identify the semantics of health care documents and clinical research papers to gain a quick and effective understanding of a patient’s history or certain medical concepts. NLP can also analyze patterns in speech for acoustic-related disorders. According to HealthITAnalytics, “Natural language processing was able to take the speech patterns of schizophrenic patients and identify which were likely to experience an onset of psychosis with 100 percent accuracy.” In addition, a study conducted by researchers from the University of Alabama found that NLP was 22.65% more accurate in identifying reportable cancer cases than the manual review of records. NLP can be the bridge between doctors and patients, providing faster and more understandable communication between both parties.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence still has a long way to go. Oftentimes, the success of an AI relies on the data collected and if the data collected is biased or small, AI algorithms lose their integrity. Researchers around the world are figuring out how to develop more accurate, intelligent, and understandable algorithms that can assist patients and medical professionals. From medical diagnosis to genetic predictions, AI is advancing the healthcare industry in unfathomable ways. AI gets a bad rap for its potential to reduce employment and its inability to understand human morals and ethics. However, in healthcare, AI can solve and perform the tasks that humans struggle to accomplish. AI has the capability to analyze millions of data points in a matter of seconds and in the healthcare industry every second counts. AI is already a part of healthcare and biomedical research. With new advancements every day, AI will continue to revolutionize the healthcare system, ultimately saving lives, time, and resources.